Table of Contents
- Works on Forward Learning
4.i. Add Your Work
4.1. Error Forward Propagation (2018)
4.2. Forward Forward (2022)
4.3. Predictive Forward Forward (2022)
4. Works on Forward Learning
A list of works on forward learning, using the forward pass for learning. Works are ordered by date.
4.i. Add your work
Contact me or submit a pull request to add a paragraph and slide on your work. The content is at your discretion. I may provide minor edits (e.g. grammar and positioning).
4.1. Error Forward Propagation (2018)
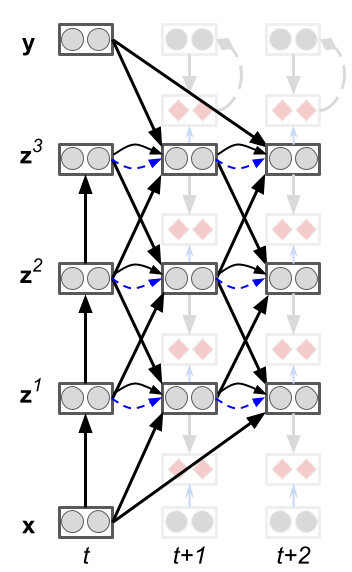
The error forward propagation algorithm is an implementation of the signal propagation framework for learning and inference in a forward pass (figure below). Under signal propagation, S is the transform of the context c, which for supervised learning is the target. In error forward propagation, S is the projection of the error from the output to the front of the network, as shown in the figure below.
Error Forward-Propagation: Reusing Feedforward Connections to Propagate Errors in Deep Learning
arxiv
4.2. Forward Forward (2022)
The forward forward algorithm is an implementation of the signal propagation framework for learning and inference in a forward pass (figure below). Under signal propagation, S is the transform of the context c, which for supervised learning is the target. In forward forward, S is a concatenation of the target c with the input x, as shown in the figure below.
Forward Forward Algorithm
arxiv
4.3. Predictive Forward Forward (2022)
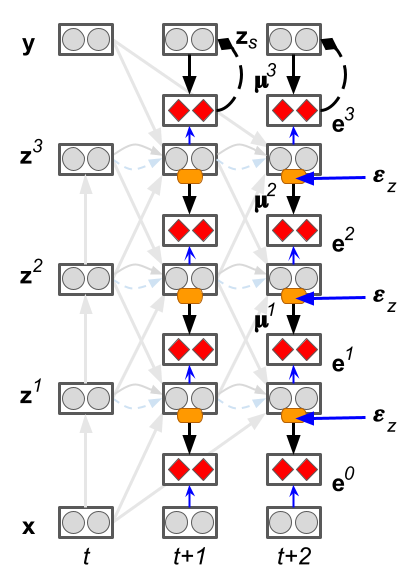
The predictive forward-forward (PFF) algorithm is a generalization of the forward-forward (FF) learning rule and predictive coding, focusing on adaptation in a recurrent neural system that combines local top-down, lateral, and bottom-up information when iteratively processing sensory patterns. PFF specifically centers around the idea that two neural circuits can jointly learn from one another, i.e., a representation circuit that focuses on rapidly acquiring representations (by contrasting positive and negative samples, as in FF) and a noisy generative circuit that focuses on synthesizing these representations (each layer of this circuit tries to locally predict the activities of the representation circuit). The top-most layer of the generative circuit contains a multimodal prior over neural activities which can then be readily sampled from in order to “fantasize” data points (based on its memories) on-the-fly. PFF notably further introduces a simple spatially and temporally local scheme for adapting cross-inhibitory and self-excitation synapses within a layer of neurons.
Predictive Forward-Forward Algorithm
arxiv
 |  |